Turkey Bacon vs. Pork Bacon
Turkey bacon nutrition facts – Choosing between turkey bacon and pork bacon often comes down to a preference for taste and a consideration of health implications. Both offer a salty, smoky flavor profile, but their nutritional compositions differ significantly, impacting their suitability for various dietary needs. This comparison will highlight the key nutritional differences to aid informed decision-making.
Nutritional Comparison of Turkey and Pork Bacon
A direct comparison reveals substantial variations in macronutrients and micronutrients between turkey and pork bacon. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed dietary choices.
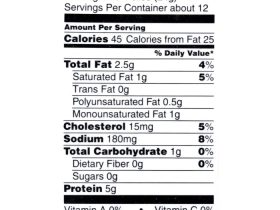
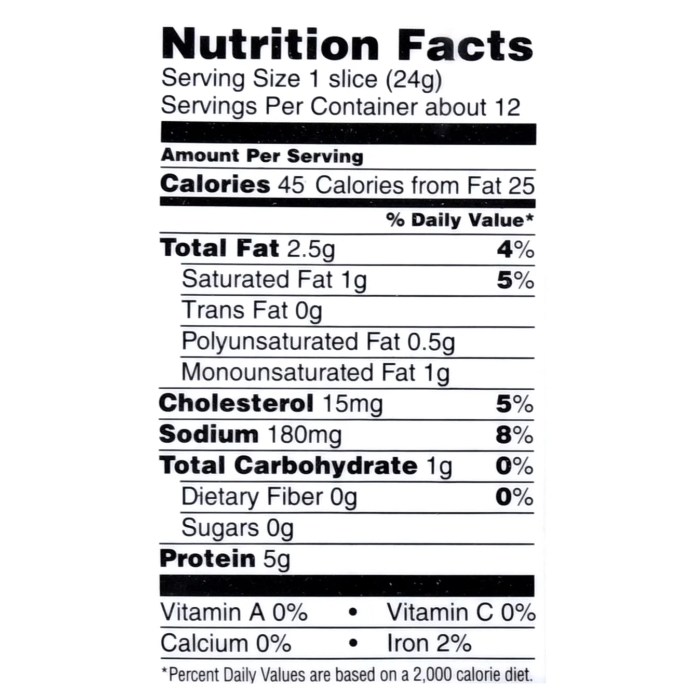
- Calories: Pork bacon generally contains significantly more calories per serving than turkey bacon. This is largely due to the higher fat content in pork bacon.
- Protein: While both offer protein, turkey bacon often boasts a slightly higher protein content per serving, making it a potentially better option for those focusing on protein intake.
- Fat: Pork bacon is considerably higher in total fat, particularly saturated fat. Turkey bacon, being leaner, has a lower overall fat content.
- Sodium: Both turkey and pork bacon are typically high in sodium. Consumers should be mindful of their sodium intake regardless of their bacon choice.
- Carbohydrates: Both types of bacon are relatively low in carbohydrates.
- Micronutrients: Both contain small amounts of micronutrients, but the quantities are generally negligible in terms of significant dietary contribution.
Saturated Fat and Cholesterol Content
The disparity in saturated fat is a primary differentiator. Pork bacon, due to its higher fat content, contains considerably more saturated fat than turkey bacon. Saturated fat is linked to increased cholesterol levels and potential cardiovascular risks. While cholesterol content varies slightly depending on the brand and preparation, pork bacon generally contains more cholesterol than turkey bacon.
This difference reinforces the cardiovascular health advantages often associated with turkey bacon.
Nutritional Advantages and Disadvantages
Choosing between turkey and pork bacon involves weighing several factors.
- Advantages of Turkey Bacon: Lower in calories, total fat, and saturated fat; often higher in protein; potentially better for heart health due to reduced saturated fat and cholesterol.
- Disadvantages of Turkey Bacon: May have a slightly different taste and texture compared to pork bacon; often contains added ingredients to enhance flavor and texture; can still be high in sodium.
- Advantages of Pork Bacon: Richer flavor and texture; provides a higher fat content which some individuals prefer.
- Disadvantages of Pork Bacon: Significantly higher in calories, total fat, saturated fat, and cholesterol; may negatively impact heart health if consumed regularly in large quantities.
Visual Comparison of Nutritional Profiles
Imagine a bar graph. The horizontal axis represents the nutrients (calories, protein, total fat, saturated fat, sodium). The vertical axis represents the quantity of each nutrient. Two sets of bars are present, one for turkey bacon and one for pork bacon. The bars representing total fat, saturated fat, and calories for pork bacon would be significantly taller than those for turkey bacon.
The protein bar for turkey bacon might be slightly taller than that of pork bacon. The sodium bars would be relatively similar in height for both. This visual representation clearly illustrates the key nutritional differences between the two types of bacon.
Understanding turkey bacon nutrition facts is crucial for mindful eating. For a comparison, you might also want to check out the nutrition facts of beef steak , as it offers a different protein source with varying fat and calorie content. Returning to turkey bacon, remember to consider serving size when assessing its overall nutritional impact.
Health Implications of Turkey Bacon Consumption
Turkey bacon offers a leaner alternative to traditional pork bacon, presenting both potential benefits and drawbacks for health-conscious individuals. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making informed dietary choices. Moderation and mindful consumption are key to maximizing potential benefits while minimizing risks.Turkey bacon, compared to pork bacon, generally contains less saturated fat and calories. This makes it a potentially better choice for those watching their weight or cholesterol levels.
However, it’s important to remember that the nutritional profile can vary significantly between brands and preparation methods.
Potential Health Benefits of Turkey Bacon
The primary health benefit of turkey bacon lies in its protein content. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function, and maintaining satiety. A serving of turkey bacon can contribute to daily protein needs, aiding in muscle growth and overall bodily function. Additionally, some brands of turkey bacon may be fortified with added vitamins and minerals, further enhancing their nutritional profile.
For example, some brands might add small amounts of Vitamin D or iron. However, it is always best to check the nutrition label to see exactly what is included.
Potential Health Risks of Turkey Bacon Consumption
Despite its lower fat content, regular consumption of turkey bacon can pose some health risks. Many brands are high in sodium, contributing to high blood pressure and increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. The high sodium content often masks other flavors, necessitating added chemicals and preservatives to improve taste. These additives, while generally considered safe in moderate amounts, are not ideal for long-term health.
The potential presence of nitrates or nitrites used as preservatives in some processed meats, is also a point of ongoing scientific discussion concerning potential health effects.
Turkey Bacon in a Balanced Diet
Incorporating turkey bacon into a balanced diet requires mindful portion control and consideration of overall dietary choices. A small serving, perhaps two or three slices, can be part of a healthy breakfast or light meal without significantly impacting overall daily sodium or fat intake. However, it should be consumed as part of a varied diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources.
Relying on turkey bacon as a primary protein source would be detrimental to a balanced and healthy diet.
Incorporating Turkey Bacon into a Healthy Eating Plan
To enjoy turkey bacon as part of a healthy eating plan, consider pairing it with nutrient-rich foods. For example, a small serving of turkey bacon can be included in a breakfast omelet with spinach and mushrooms, or as part of a salad with plenty of vegetables and a light vinaigrette. Always check nutrition labels to choose lower-sodium options, and be mindful of portion sizes to manage sodium and calorie intake effectively.
Turkey Bacon and Dietary Restrictions: Turkey Bacon Nutrition Facts
Turkey bacon, a popular alternative to pork bacon, offers a potentially healthier option for many, but its suitability depends heavily on individual dietary needs and restrictions. Understanding its nutritional profile is crucial for making informed choices. This section explores how turkey bacon aligns with various dietary plans and potential considerations for those with specific dietary restrictions or allergies.
Turkey Bacon and Low-Fat Diets
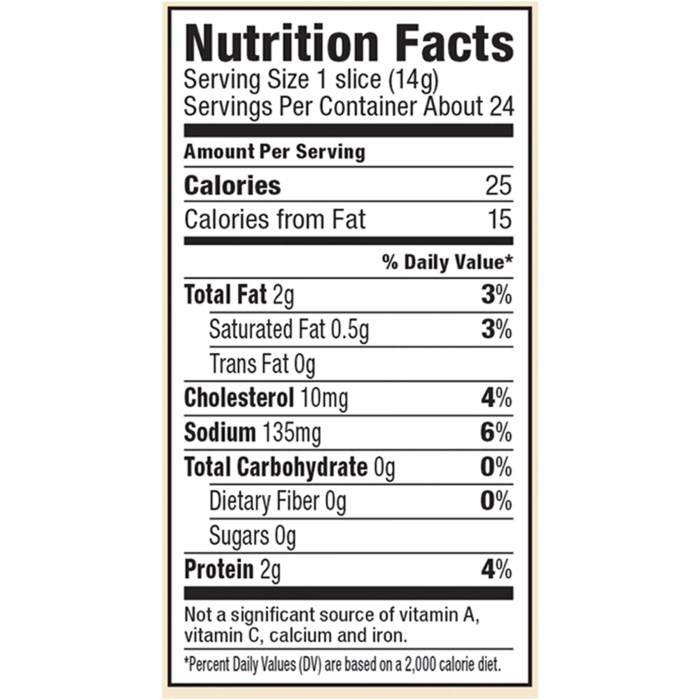
Turkey bacon generally contains less fat than pork bacon. A typical serving of turkey bacon has significantly fewer grams of total fat and saturated fat compared to its pork counterpart. This makes it a more suitable choice for individuals following a low-fat diet, aiming to reduce their overall fat intake for heart health or weight management. However, it’s important to note that even turkey bacon contains some fat, and portion control remains essential.
For example, while a serving of pork bacon might contain 15g of fat, a similar serving of turkey bacon might contain only 5g, a considerable difference.
Turkey Bacon and Low-Sodium Diets
Sodium content can vary significantly between brands and types of turkey bacon. Some brands offer reduced-sodium options specifically for individuals monitoring their sodium intake due to high blood pressure or other health concerns. Always check the nutrition label to compare sodium content across different brands before making a purchase. Choosing low-sodium options can help those on a low-sodium diet manage their sodium intake effectively.
For instance, one brand might offer a product with 200mg of sodium per serving, while another might contain 400mg.
Turkey Bacon and Ketogenic Diets, Turkey bacon nutrition facts
Turkey bacon is generally compatible with ketogenic diets. Its high protein and fat content, along with its low carbohydrate count, makes it a suitable addition to keto-friendly meal plans. However, the carbohydrate content can vary slightly depending on the brand and processing methods. Individuals following a strict ketogenic diet should always check the nutrition label to ensure the carbohydrate content aligns with their daily macro targets.
The high protein content also helps with satiety and supports muscle mass maintenance, beneficial aspects of a ketogenic lifestyle.
Turkey Bacon and Diabetes
For individuals with diabetes, the lower fat and potentially lower sodium content of turkey bacon compared to pork bacon can be advantageous. However, portion control remains crucial to manage blood sugar levels. The protein content can contribute to feeling full and help prevent blood sugar spikes. It is important to incorporate turkey bacon as part of a balanced meal plan that includes other components like non-starchy vegetables and healthy fats to achieve better glycemic control.
Consulting a registered dietitian or diabetes educator is recommended to determine the appropriate portion sizes and integration of turkey bacon into an individual’s diabetic meal plan.
Turkey Bacon and Heart Disease
The lower fat content of turkey bacon compared to pork bacon might offer some benefits for individuals with heart disease, particularly by reducing saturated fat intake. However, the sodium content should be carefully monitored, as high sodium intake can negatively impact cardiovascular health. Choosing low-sodium options and controlling portion sizes are essential considerations. Incorporating turkey bacon as part of a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while limiting saturated and trans fats, is crucial for heart health management.
Dietary advice from a healthcare professional is essential for individuals with heart disease.
Turkey Bacon and Allergens
Potential allergens in turkey bacon include soy (often used as a binder), milk (used in some processing), and gluten (if cross-contamination occurs during processing). Individuals with allergies should carefully check the ingredient list on the packaging to identify potential allergens. Always be cautious of cross-contamination, particularly in food processing facilities that handle multiple products containing allergens. For individuals with severe allergies, it’s crucial to choose brands that clearly label allergen information and follow strict dietary protocols to minimize the risk of allergic reactions.
FAQ Overview
What are the best brands of turkey bacon for low sodium diets?
Several brands offer lower-sodium options; check nutrition labels to compare sodium content per serving. Look for brands explicitly marketing “low sodium” or “reduced sodium” varieties.
Can I eat turkey bacon if I’m diabetic?
Turkey bacon can be part of a diabetic diet, but portion control is vital due to its carbohydrate and fat content. Consult your doctor or a registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice.
Is turkey bacon suitable for a ketogenic diet?
Generally, yes, as it’s relatively low in carbohydrates. However, always check the specific carbohydrate content per serving to ensure it aligns with your daily ketogenic macro targets.
Does cooking method significantly alter turkey bacon’s nutritional content?
Yes, methods like frying can increase fat content compared to baking or microwaving. Baking or microwaving generally preserves more nutrients.
What are common allergens found in turkey bacon?
Soy and milk are potential allergens, though this varies depending on the brand and processing methods. Always check the ingredient list for potential allergens.